
The Gut-Brain Axis: Exploring the Connection Between Gut Health and Mental Well-being
Introduction: The gut-brain axis (GBA) is a fascinating area of research that investigates the intricate relationship between the brain, gut, and microbiome, and its profound impact on our overall health. This bidirectional communication system, comprising the central nervous system, enteric nervous system, and gut microbes, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
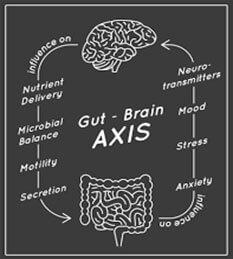
The Gut-Brain Axis and Its Significance: The brain and gut are intricately linked through the GBA, which facilitates communication between the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system consists of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons embedded in the gastrointestinal tract, connecting cognitive and emotional centres in the brain with peripheral intestinal functions. This complex interaction involves the endocrine, immune, and autonomic nervous systems, influencing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, and colitis.
The Role of Gut Microbiota: The gut microbiota refers to the diverse collection of microorganisms inhabiting the gastrointestinal tract. The composition of this microbial community is unique to each individual and undergoes evolution throughout their lifetime. Studies have shown that the gut microbiota plays a vital role in the development and maturation of the central nervous system and enteric nervous system during early postnatal weeks.
The human gut houses an estimated 500 to 1,000 bacterial species, outnumbering human cells by approximately tenfold. The gastrointestinal tract, with its vast surface area, serves as a primary site for microbial colonization. The balance of the gut microbiota, along with the presence or absence of specific species, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and influencing the intestinal mucosa and beyond. The most dominant bacterial phyla in the gut are Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes.
Production of Microbial Metabolites: Certain bacteria in the gut, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, produce essential neurotransmitters like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), serotonin, and dopamine. Additionally, bacterial production of short-chain fatty acids can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system and influence brain functions like memory and learning. The gut microbiota also regulates tryptophan levels, a precursor to serotonin, impacting mood and cognition.
Incorporating Probiotics into Your Routine: The gut and brain are connected through various mechanisms. The vagus nerve serves as a major pathway, transmitting signals between the gastrointestinal tract, heart, lungs, and brain. Sensory neurons carry feedback from the gut to the brain stem, engaging brain regions responsible for hunger and emotions. Neuroendocrine signalling, involving neuropeptides, and the gut-associated lymphoid tissue, which comprises a significant portion of the immune system, also contribute to the gut-brain connection.
Health Implications: The gut-brain axis has significant implications for our overall health and mental well-being. Disruptions in this axis can lead to conditions like depression, anxiety, and digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome. Research suggests that maintaining a healthy GBA is crucial for optimal brain function and behaviour. Diet plays a fundamental role in supporting a functional GBA, and a balanced diet rich in fish, vegetables, cereals, fruits, and water is recommended. Improving one's diet may benefit individuals experiencing depression, as a healthy gut-brain axis can positively influence mental health.
Promising Treatment Targets: The study of the GBA has revealed exciting potential for novel treatment targets in functional gastrointestinal disorders, as well as various psychiatric and neurological conditions. Conditions like Parkinson's disease, autism spectrum disorders, anxiety, and depression are being explored in preclinical and clinical studies, highlighting the role of the GBA in their pathophysiology.
Conclusion: Understanding the gut-brain axis and its impact on our health is an ongoing field of research. The bidirectional communication between the gut, brain, and microbiome has far-reaching implications for mental well-being, digestive health, and overall bodily functions. By nourishing our gut microbiota through a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, we can support a thriving gut-brain axis and promote optimal health and well-being.
